Getting Started¶
Why airflow-balancer?¶
airflow-balancer provides utilities for tracking hosts, ports, and load balancing within Apache Airflow DAGs. It enables you to:
Track Hosts: Define and manage a pool of worker hosts with different capabilities (OS, queues, tags)
Manage Ports: Track port usage across your host infrastructure to avoid conflicts
Load Balance: Intelligently select hosts based on queues, operating systems, tags, or custom criteria
Integrate with Airflow: Automatically create Airflow pools for each host and port, providing built-in resource management
Key Benefits:
Declarative Configuration: Define your host infrastructure in YAML configuration files
Automatic Pool Management: Pools are automatically created and managed in Airflow for each host
SSH Integration: Built-in SSH hook generation for seamless operator integration
Flexible Selection: Query hosts using queues, OS, tags, or custom filter functions
Visual Management: Built-in Airflow plugin and standalone viewer for infrastructure visualization
Integration with airflow-laminar Stack¶
airflow-balancer is tightly integrated with other libraries in the airflow-laminar ecosystem:
airflow-pydantic¶
The core data models (Host, Port, BalancerConfiguration) are defined in airflow-pydantic. This ensures:
Full Pydantic validation and type checking
JSON/YAML serialization support
Consistent model behavior across the stack
airflow-config¶
airflow-balancer uses airflow-config for configuration loading via Hydra. This allows:
Hierarchical configuration with defaults and overrides
Environment-specific configurations (dev, staging, production)
Integration with the broader Airflow configuration ecosystem
Installation¶
Install from PyPI:
pip install airflow-balancer
Or via conda:
conda install airflow-balancer -c conda-forge
Optional Dependencies¶
For use with Apache Airflow 2.x:
pip install airflow-balancer[airflow]
For use with Apache Airflow 3.x:
pip install airflow-balancer[airflow3]
Basic Usage¶
Standalone Configuration¶
You can load a balancer configuration directly from a YAML file:
from airflow_balancer import BalancerConfiguration
# Load from a YAML file
config = BalancerConfiguration.load_path("config/balancer.yaml")
# Select a host from the 'workers' queue
host = config.select_host(queue="workers")
# Get a free port on that host
port = config.free_port(host=host)
# Use the host's SSH hook with an operator
from airflow.providers.ssh.operators.ssh import SSHOperator
operator = SSHOperator(
task_id="run_on_worker",
ssh_hook=host.hook(),
command="echo 'Hello from worker!'",
)
With airflow-config (Recommended)¶
The recommended approach is to use airflow-balancer as an extension within your airflow-config configuration:
# config/config.yaml
# @package _global_
_target_: airflow_config.Configuration
defaults:
- extensions/balancer@extensions.balancer
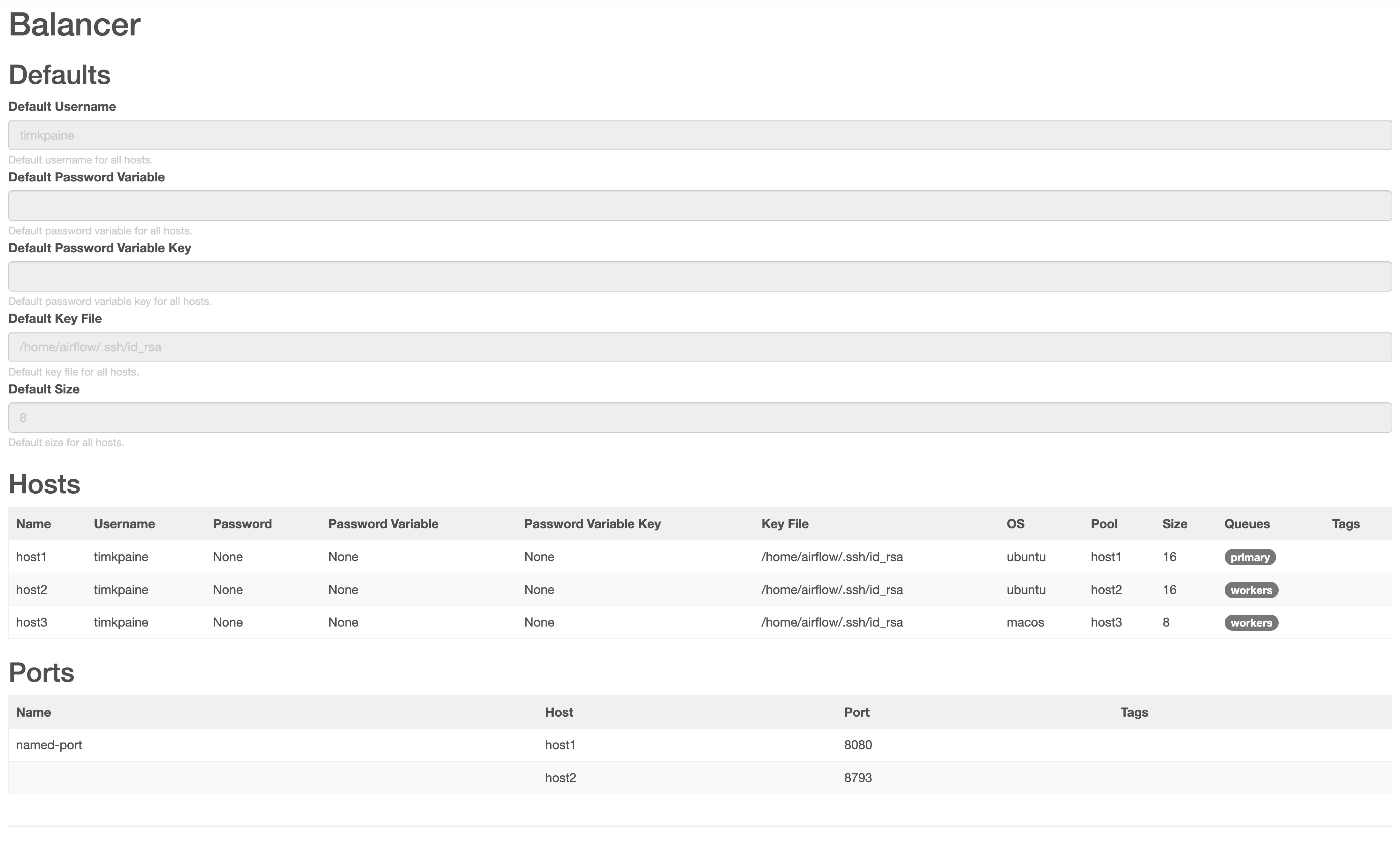
# config/extensions/balancer.yaml
# @package extensions.balancer
_target_: airflow_balancer.BalancerConfiguration
default_username: airflow
default_key_file: /home/airflow/.ssh/id_rsa
primary_queue: primary
secondary_queue: workers
hosts:
- name: host1
size: 16
os: ubuntu
queues: [primary]
- name: host2
os: ubuntu
size: 16
queues: [workers]
- name: host3
os: macos
size: 8
queues: [workers]
ports:
- host_name: host1
port: 8080
- host_name: host2
port: 8793
# dags/my_dag.py
from airflow_config import load_config
from airflow_balancer import BalancerConfiguration
# Load via airflow-config
config = load_config("config", "config")
balancer: BalancerConfiguration = config.extensions["balancer"]
# Now use the balancer
host = balancer.select_host(queue="workers", os="ubuntu")
Creating Hosts Programmatically¶
from airflow_balancer import BalancerConfiguration, Host
from airflow_balancer.testing import pools
# Create configuration programmatically
config = BalancerConfiguration(
default_username="airflow",
hosts=[
Host(name="worker1", os="ubuntu", size=8, queues=["compute"]),
Host(name="worker2", os="ubuntu", size=16, queues=["compute"]),
Host(name="gpu-node", os="ubuntu", size=4, queues=["gpu"], tags=["cuda"]),
],
)
# Filter hosts by criteria
ubuntu_hosts = config.filter_hosts(os="ubuntu")
compute_hosts = config.filter_hosts(queue="compute")
gpu_hosts = config.filter_hosts(tag="cuda")
# Select a single host (randomly chosen from matches)
selected = config.select_host(queue="compute")
Visualization¶
airflow-balancer includes a built-in UI for viewing your host and port configurations.
Airflow Plugin¶
The plugin adds a menu item to the Airflow toolbar:
Home View¶
Host Details¶
Standalone Viewer¶
You can also run the viewer as a standalone application:
airflow-balancer-viewer
Next Steps¶
See the Examples page for more detailed usage patterns
Check the API Reference for complete API documentation